python3系列(1)-pip、内置对象、运算符
##python:一种解释型、面向对象、动态数据类型的高级程序设计语言
计算机的存在是为了计算数据、存储数据 计算数据存储在内存中,持久化存在硬盘上
pip管理扩展库
1、常用命令
pip download package[==version]
pip freeze [> requirements.txt]
pip list
pip install package[==version]
pip install package.whl
pip install -r requirements.txt
pip install --upgrade package
pip uninstall package[==version]
2、使用配置文件配置更改下载源
[global]
trusted-host=mirrors.aliyun.com
index-url=http://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/
配置文件放置位置
Linux下: ~/.pip/pip.conf
windows下:用户文件夹下\pip\pip.ini
3、使用命令行临时改变pip源
pip install -i <mirror> --trusted-host <mirrorhost> package
例如
pip install -i http://pypi.douban.com/simple/ --trusted-host pypi.douban.com pandas
国内源:
- http://pypi.v2ex.com/simple/
- http://pypi.douban.com/simple/
- http://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/
内置对象
- python严格区分大小写,
- 变量不需要提前声明,直接赋值使用
- python动态类型语言,变量的类型可随时变化
对象类型:数字(int,float,complex)、字符串(str)、字节串(bytes)、列表(list)、字典(dict)、元组(tuple)、集合(set、frozenset)、布尔型(bool)、空类型(NoneType)、异常、文件、其他迭代对象、编程单元
- 字符串以r开头包括,表示忽略转义的原始字符串
- 字符串通过encode方法可以转成字节串,字节串通过decode方法转成字符串
- 字节串以b引导
- 元组如果只有一个元素时,逗号不可省略
- 集合内所有元素都不可重复,set元素可变,frozenset元素不可变
- 布尔型只有True和False两个值,区分大小写
- 生成器对象、range对象、zip对象、enumerate对象、map对象、filter对象具有惰性求值的特点,每当使用时才取到值,用完就不再在对象里
>>> r = zip("abc","12")
>>> ("a","1") in r
True
>>> ("a","1") in r
False
- 不可变对象:数字、字符串、元组、frozenset
- 可变对象:列表、集合、字典
- 查看所有关键字,使用keyword.kwlist
- 查看所有内置对象
dir(__builtins__) - 使用id(x)查看x的内存地址
- 使用ord(‘A’)求字符A对应的unicode码,chr(65)返回unicode码65对应的字符
python运算符
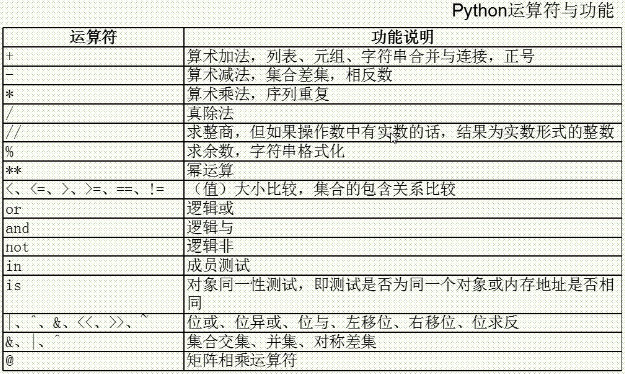
- +运算符除了算术运算外,还支持同类型对象拼接
>>> [1,2,3]+["a","b"]
[1, 2, 3, 'a', 'b']
>>> "A"+1
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: must be str, not int
>>> True+3
4
>>> False+3
3
- *运算符不仅用于乘法,还用于重复对象
>>> "a"*10
'aaaaaaaaaa'
>>> [1,2,3]*3
[1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3]
>>> (1,2,3)*3
(1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3)
- 字符串比较大小,按字符位,逐个比较
>>> 'Hello'>'world'
False
>>> ord("H")
72
>>> ord("w")
119
- map使用,对后一个参数的元素都使用前面的函数
>>> c = [1,2,3,4]
>>> d = list(map(str,c))
>>> d
['1', '2', '3', '4']
- 数字与字符可直接互换,但是列表与字符串不能互换
>>> str([1,2,3])
'[1, 2, 3]'
>>> list(str([1,2,3]))
['[', '1', ',', ' ', '2', ',', ' ', '3', ']']
>>>
>>> eval(str([1,2,3]))
[1, 2, 3]
-
python3中input()不管输入什么,都作为字符串形式赋予变量
-
python3中将内容打印到文件的示例,注意关闭文件时,缓存才落到磁盘上
>>> fp=open(r'D:\mytest.txt','a+')
>>> print('Hello world!',file=fp)
>>> fp.close()
-
模块导入查询,
import sys;print(sys.modules.items),增加模块导入的查询路径在sys.path后append要添加的路径 -
模块搜索的顺序:当前文件夹 » sys.path变量指定的文件夹 » 优先导入pyc文件